Introduction
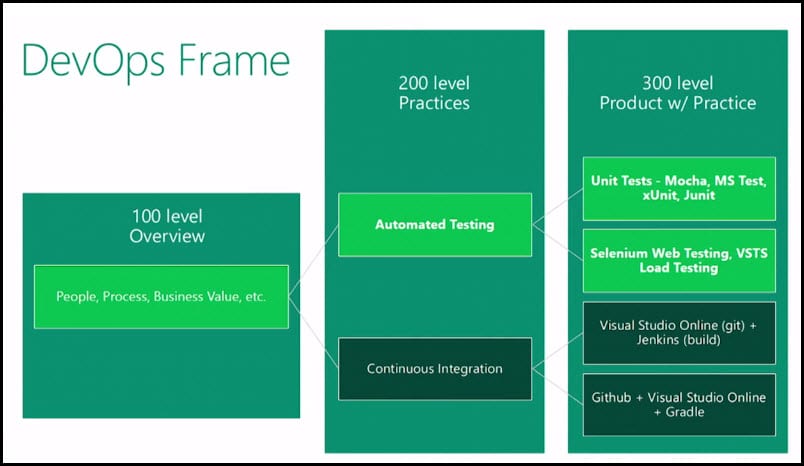
Automated testing is a very extensive topic, so in this blog post, I'll just summarize the most important parts of Automated testing. Software testing is present in almost every cycle of software development. From DevOps view, the software testing is mapped to practices and then to actual technologies which can be used for implementation, as shown in the image below. The key point of 100 Level is rapid deployment and production with high quality. From here the practice of Automated testing comes into 200 Level. From here the Automated testing can be mapped to numerous processes and tools for implementation, such as Unit and Load testing.
You can find more information about DevOps
in the following post: DevOps: The Three Stage Conversation - People, Process, Products which describes the basic principles of DevOps. This post will be especially helpful to those for whom DevOps is still a new concept. If you prefer a deeper view on this topic, have a look at the following guide: quick guide about Basic Principles of DevOps, which presents an overview of DevOps process and practices, describing "the big picture", while still maintaining the high level of detail.
The purpose of running Automated tests it to run tests agile and frequently. In particular, when testing in an agile environment, it's not only required to adopt quickly to software changes, it's necessary. There are many benefits for running Automated tests, such as:
- Speed optimization and efficiency;
- Maintaining and improving quality;
- Cost reduction;
- Test coverage expansion;
- Reusability, reliability, and continuity;
- Boosting tester's encouragement and efficiency.
You can see this video if you would like to find more information about how to generate unit tests and calculate the code coverage on the local machine, and how to perform the same process with VSTS and the Build on the cloud. You will see how to add your existing projects to VSTS. How to use Console.Read() function to prevent your app from closing and to add a new project and create a hand-coded unit test in that project, and finally to generating++ unit tests with Intelli Test . Which scans the code and suggests you all the possible unit testing cases. You will see the comparison of the Code Coverage of the hand-coded test with the generated unit test, the latter providing 100% Code Coverage.
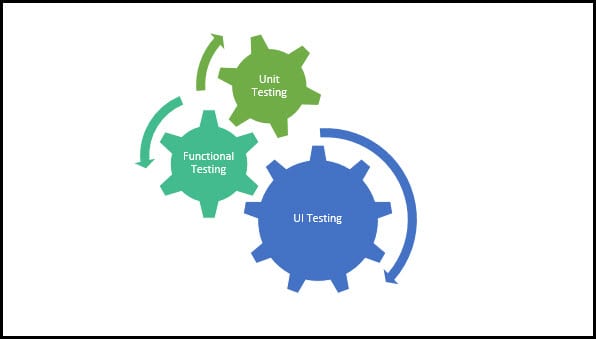
Types of Automated testing
As already explained in post Introduction to software testing the Automated test will run by a computer, but they will be created by the tester, which can create the test in the way that it will run every time when code or part of it will be changed. There are several particular types of software tests, which can be Automated.
If you would like to know more about the best practices for DevOps, Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery, you can have a look at the following post: Configure CI (Continuous Integration) and CD (Continuous Delivery Pipeline).
UI Testing
Automated UI testing is also known as coded UI test and they perform functional testing of a user interface. Such as testing a web page. These tests are very useful, very easy to implement and they can be easily modified to suit the project. It's very important to emphasize that they allow for both. Tester and developer to work with the same tools or language, which is improving the efficiency of both sides.
Unit Testing
The word "Unit" is already pointing that this type of software testing is used to test the small units. Such as a piece of code, a function, a method, class or any other property. This type of testing is used already in early stages of software development and it's each test case is usually self-reliant. The purpose of Unit testing is to isolate parts of the software and to present the functionality of individual parts.
Functional Testing
Functional testing represents the testing of software with the purpose to ensure that the tested software is meeting all functional requirements. It's basically testing of application in relation to its end users and to the rest of the system. Is a type of Black-Box testing in which the tester doesn't have any insights about software and its functionally. Under Functional Testing, there are also some other types, such as:
Smoke testing
- which is software testing of most essential functions of a software, but not interfering with other smaller details. The term comes from hardware testing, where if the test didn't pass the smoke
Regression testing is done to check if the software still works even after the newly implemented changes. It's usually done after changing or adding new code, which can easily produce new bugs or changes that were not intended to be changed.
Usability testing is done with the purpose of evaluating the product through users. It's executed with real users in order to estimate the usability of the product.
Data Driven Testing is used when external data are loaded to existing functional test in order to extend Automated test cases. Test scripts contain test data with output values which are readable from data files, such as CVS files, Excel, CVS files, etc.
- Keyword Testing where the keywords are specified for each action in the test case. The keywords can be keystrokes, mouse click or other action. Every keyword or set of keywords is then associated to function or action. This type of testing doesn't require any programming skills as it's very easy to design such test cases, so it's very appropriate type of testing for new testers or non-technical ones.
In order to ensure Continuous Integration, we need to use proper deploying strategy. Read more about deploying with Feature Branches and Feature Toggle in the following post; Deploy from Branches with and without Feature Toggle.
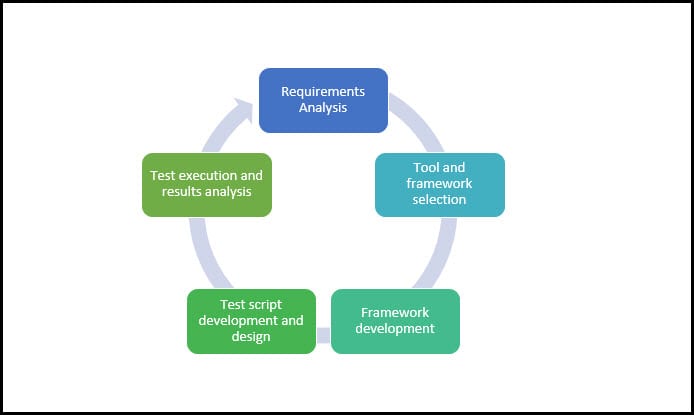
Planning and Executing Automated Tests
The first step is to review and to define the needs and the requirements of the application and to confirm if the application is suited for Automated testing. Once when the Automated testing for application confirms the proper tool should be selected for test execution. Here is important also to classify the appropriate framework, which is basically a set of automation guidelines. After that, the scope of automation can be set. The scope of automation will define which features are important, technical usefulness, types of data in different scenarios and the complexity of each test case. It's important also to determine the automation strategy, which will define the design of framework, tools for automation and schedule for execution. After all key factors are well defined the crucial step is to develop appropriate automation framework. If you are using Visual Studio tools, you will find many projects templated and frameworks already build it and they are supporting various platforms. The last step of the process is to develop a Test script in order to define a set of instruction to be performed during the test execution.
Conclusion
Automated testing is a good choice where tests should be performed frequently and quickly. Usage of Automated tests can save tons of money and time and furthermore, it highly increases the test coverage. Automated tests can be run unattended and they are flexible and maintainable. However, it's important to note that Automated tests should be created by a developer. Which is not the case in manual testing where the testing can be performed by tester without any programming skills. It's important also to highlight that in some smaller projects. Where the testing is not so rapid, the development of Automated testing. can easily overweight the benefits against the cost, so in such cases. It's better to consider manual testing. Furthermore the Automated testing is in companionship with manual testing and it's not replacing it. It's considered to be a complement on top of manual testing.
The key benefits of Automated testing are:
- Running on multiple machines with different configuration;
- Obtaining Code coverage metrics in time when Automated tests are running;
- Helping to maintain stability;
- Execution of many different complex cases in every run, with coverage which is inaccessible in manual testing.