Introduction
In this post, I am going to introduce you to Azure DevOps, a set of cloud-hosted DevOps services that work for any language, targeting any platform. With Azure DevOps, you can turn an idea into a working piece of software. You can plan your project with agile tools, manage your test plans from the web, version your code using Git, and deploy your solutions to an incredible cross-platform CI/CD system. You can do all of this while getting full traceability and visibility across your development activities.
For more information about how to work with Kubernetes clusters and deploy them to Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and work with Azure Container Registry, see Kubernetes cluster for beginners
How to access your organizations and projects
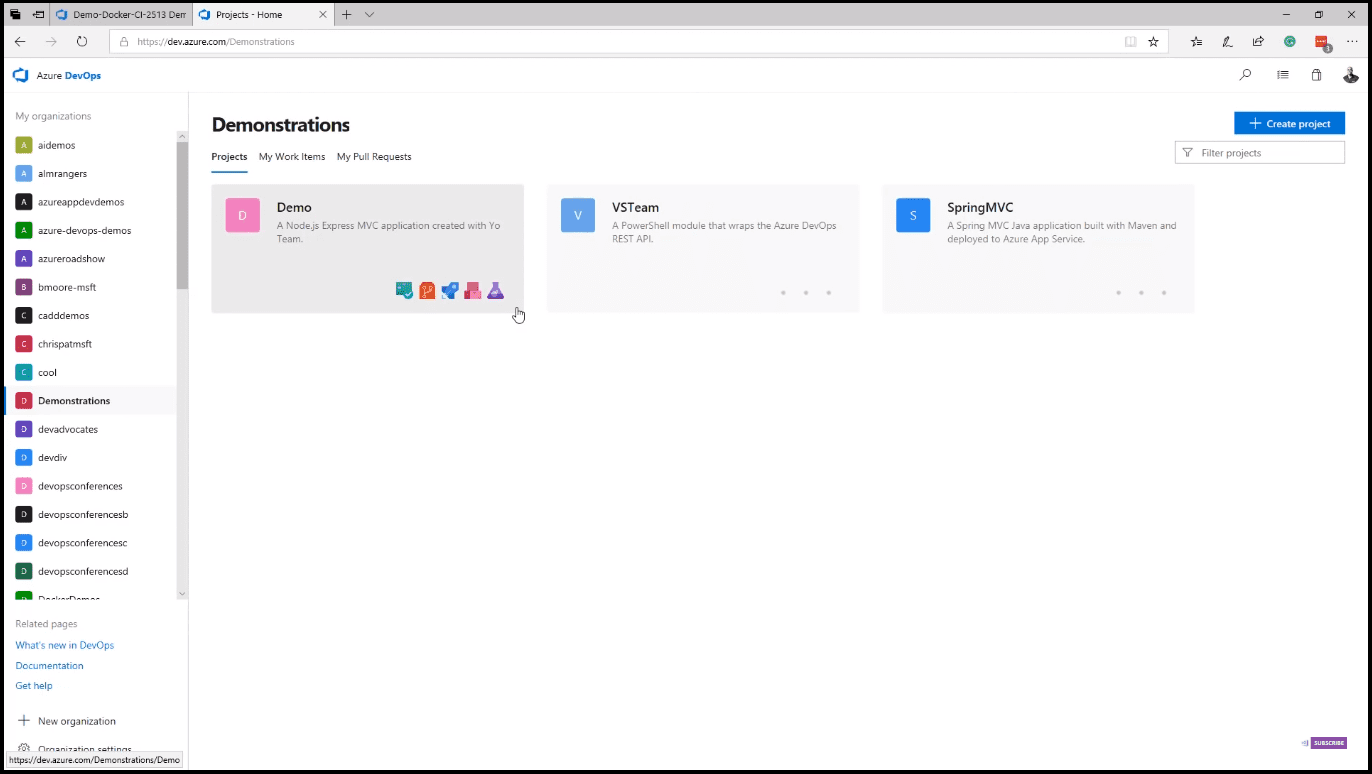
Go to dev.azure.com, and your Azure DevOps page with Demonstrations will open. From the Demonstrations page, you can see your Projects, your Work Items, and your Pull Requests. On the Projects page, as you hover over the tiles (image 1), you can see which services each project uses. You can use as much or as little of Azure DevOps as you need.
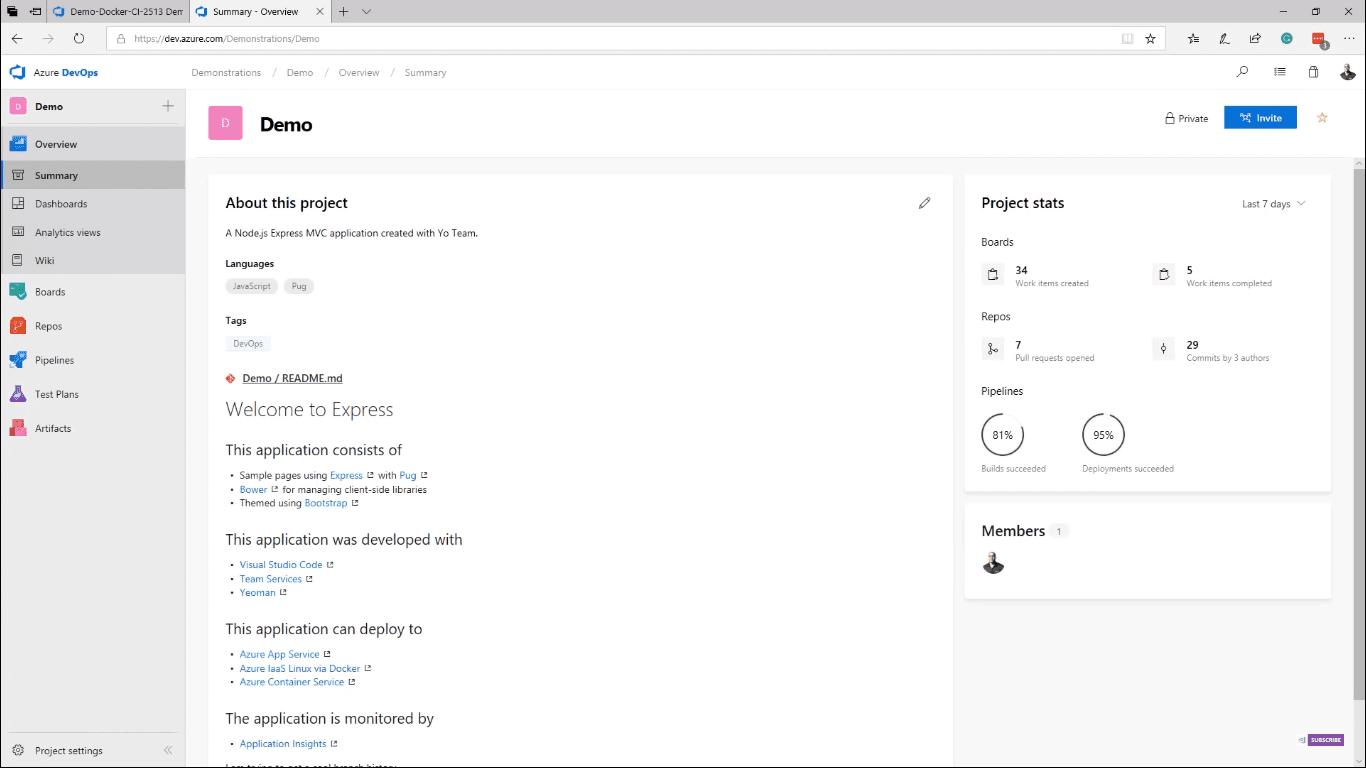
On the My Work Items page, you can see all work that is assigned to you, and on the My Pull Request page, you can see all pull requests that need your attention. Clicking on the Projects tile takes you to the Summary page, where you can quickly see the description of the project, project stats, and team members (image 2).
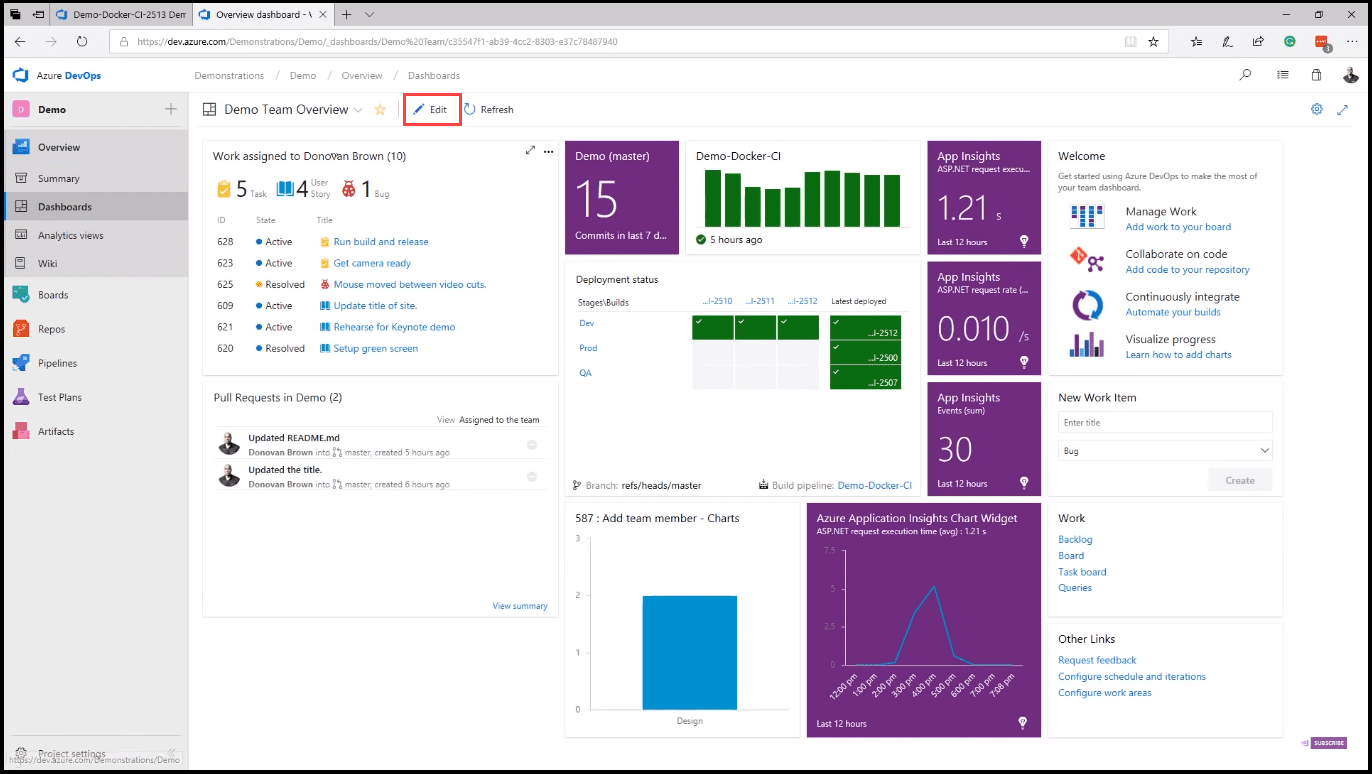
From the left navigation, you can access the Dashboards page. Dashboards are fully customizable. Simply click on the Edit button (image 3), and drag and drop the desired widget. Additional widgets are available from VS Marketplace.
The widgets are interactive; for example, you can use the new work item widget to create a new item or click the board link on the Work widget to jump to your Kanban board.
Kanban boards and backlogs
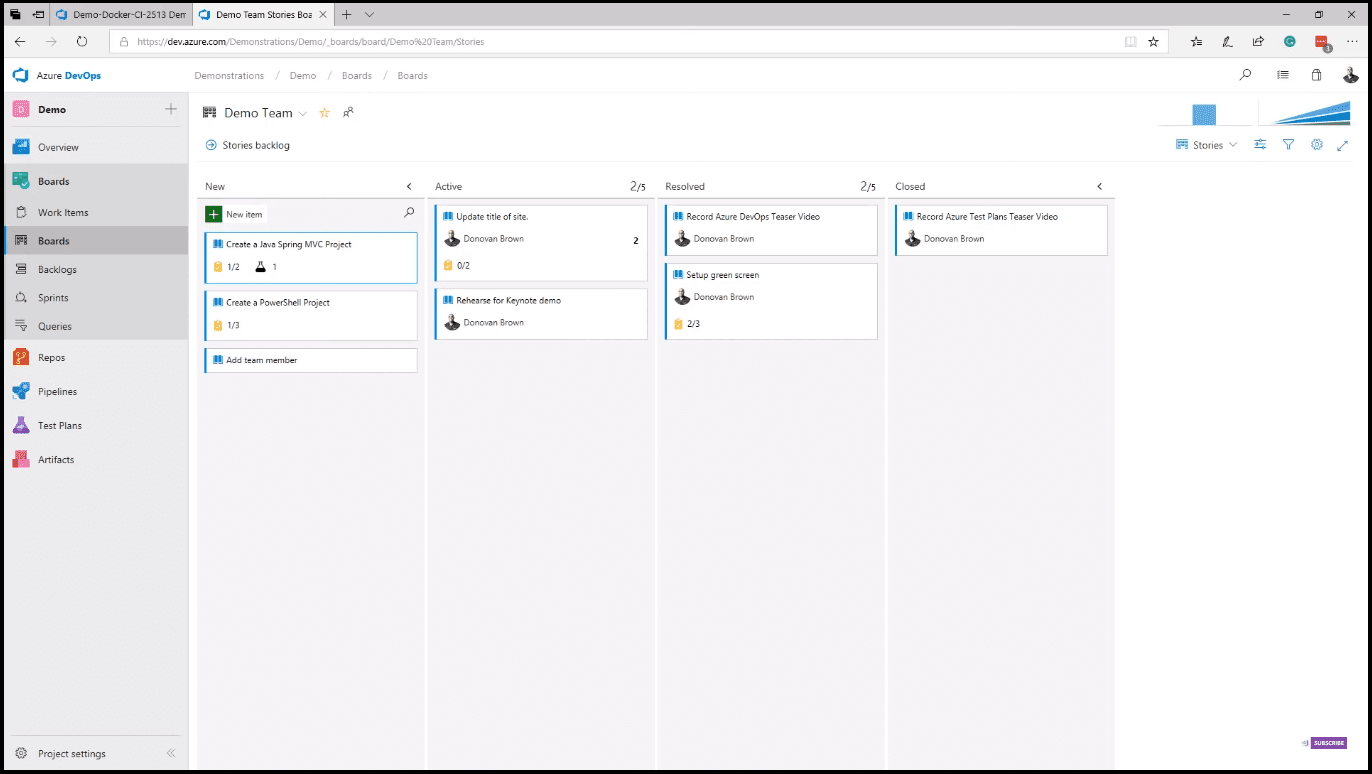
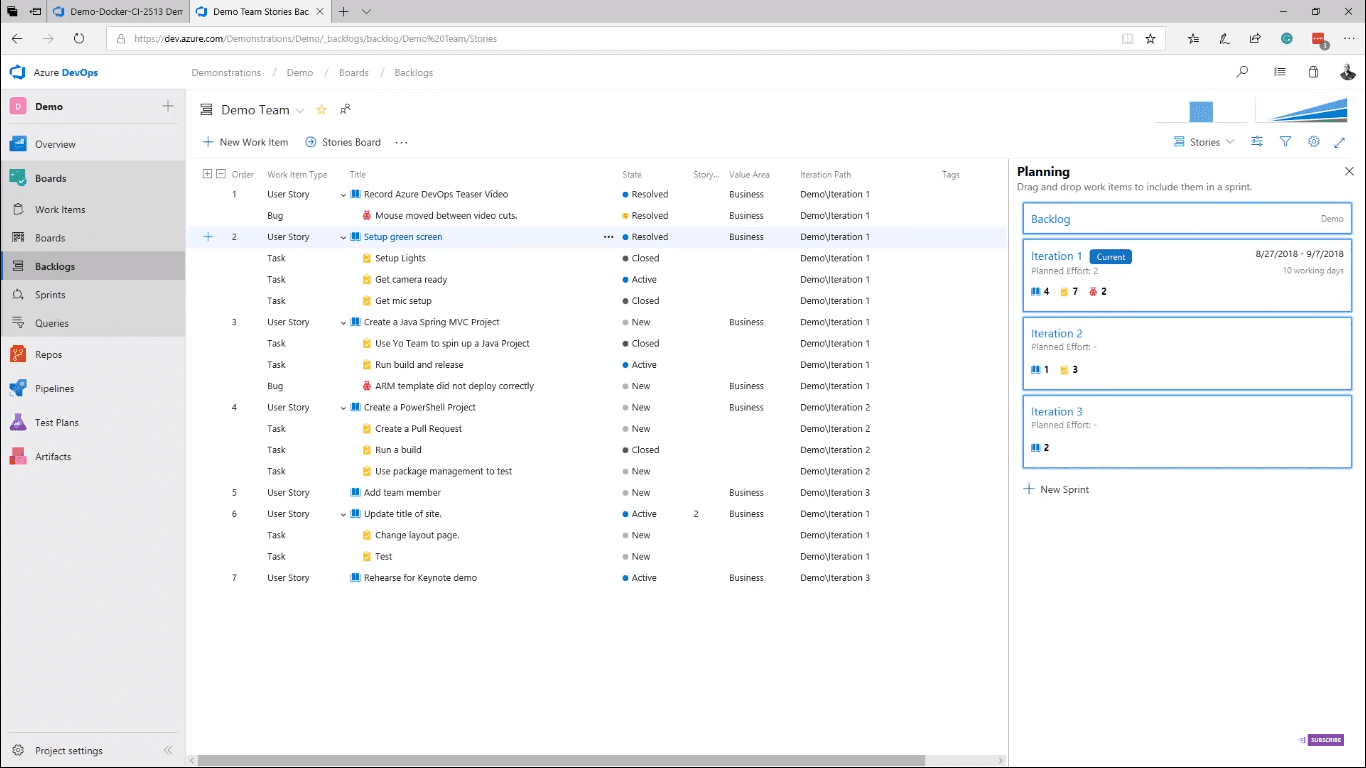
The Kanban board is a feature of Azure Boards, which allows you to plan your project using backlogs and boards (image 4). You can plan and track your entire release. From the Kanban boards, you can review your tests and tasks for each item.
Using the backlogs (image 5), you can plan your Sprints by dragging and dropping an item to the desired sprint. Once in a sprint, you can use the Task board to track the progress. As engineers start a task, they can easily create branches for their work right from the board.
For more information about how to work with Git using animation, with all commands represented in graphical animation (e.g., git branch, git merge, git rebase, git cherry-pick), see Mastering Git with animation
Azure Repos, Files, Commits, Pushes, and Tags
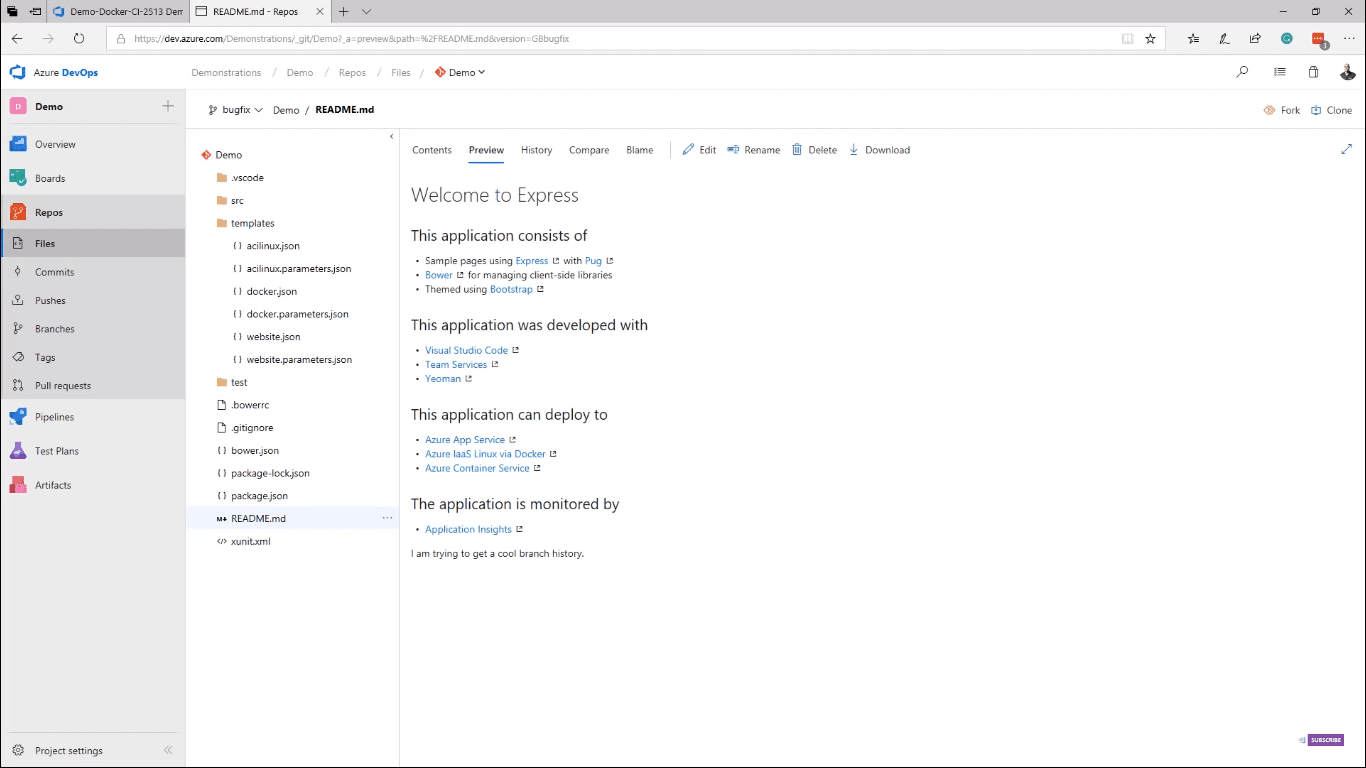
This brings us to Azure Repos, which supports both centralized version control (TFVC) and distributed version control (Git). From Files, you can navigate to your repo’s content and even make quick edits (image 6).
Commits allow you to see how all your branches come together. Pushes give you a historical view of the changes pushed to the remote repository, while branches allow you to review all the branches and see if they are ahead or behind the master. The Tags page not only allows you to review your tags but also create new ones. Using the pull request page, you can review and participate in pull requests. As your repositories allow you to leave rich comments during your pull requests, you can even apply policies that require a build to be executed.
Azure Pipelines
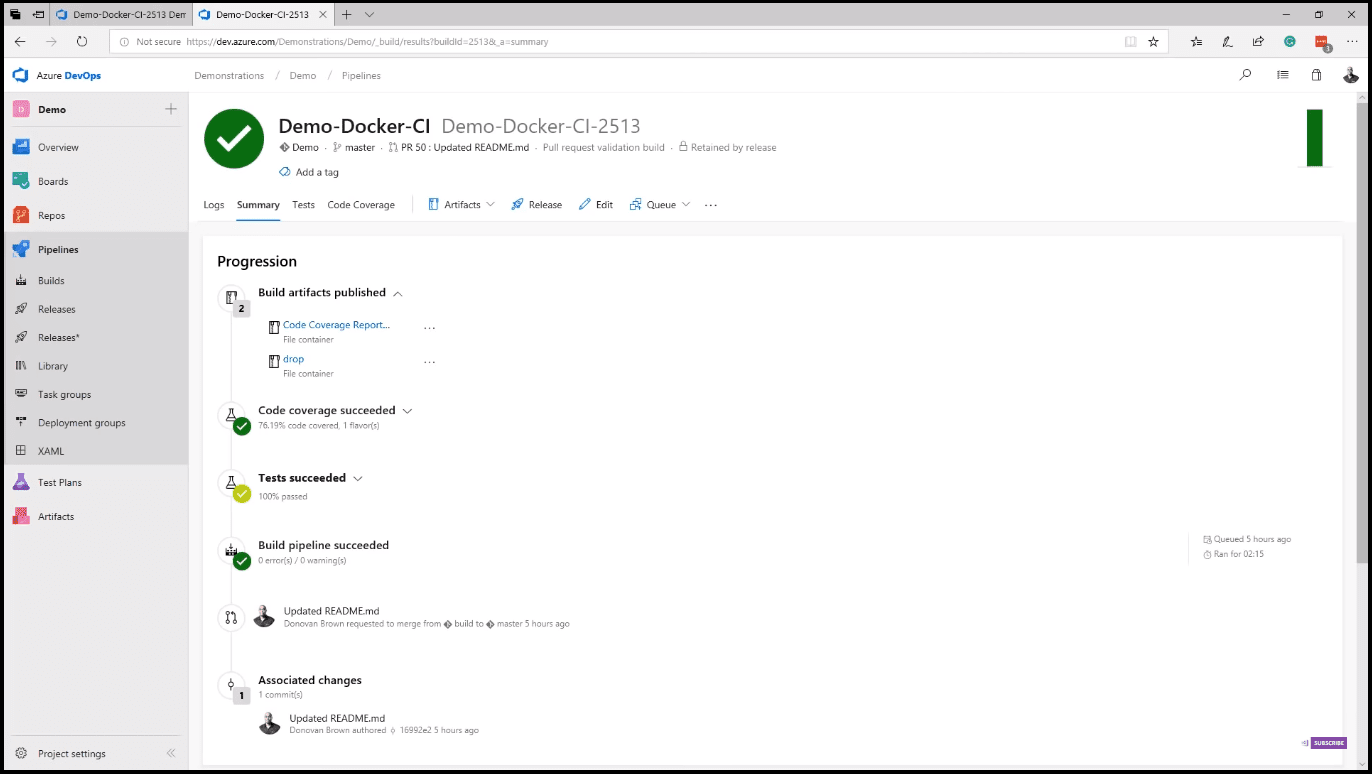
Azure Pipelines is a rich cross-platform CI/CD system, capable of building any language targeting any platform (image 7).
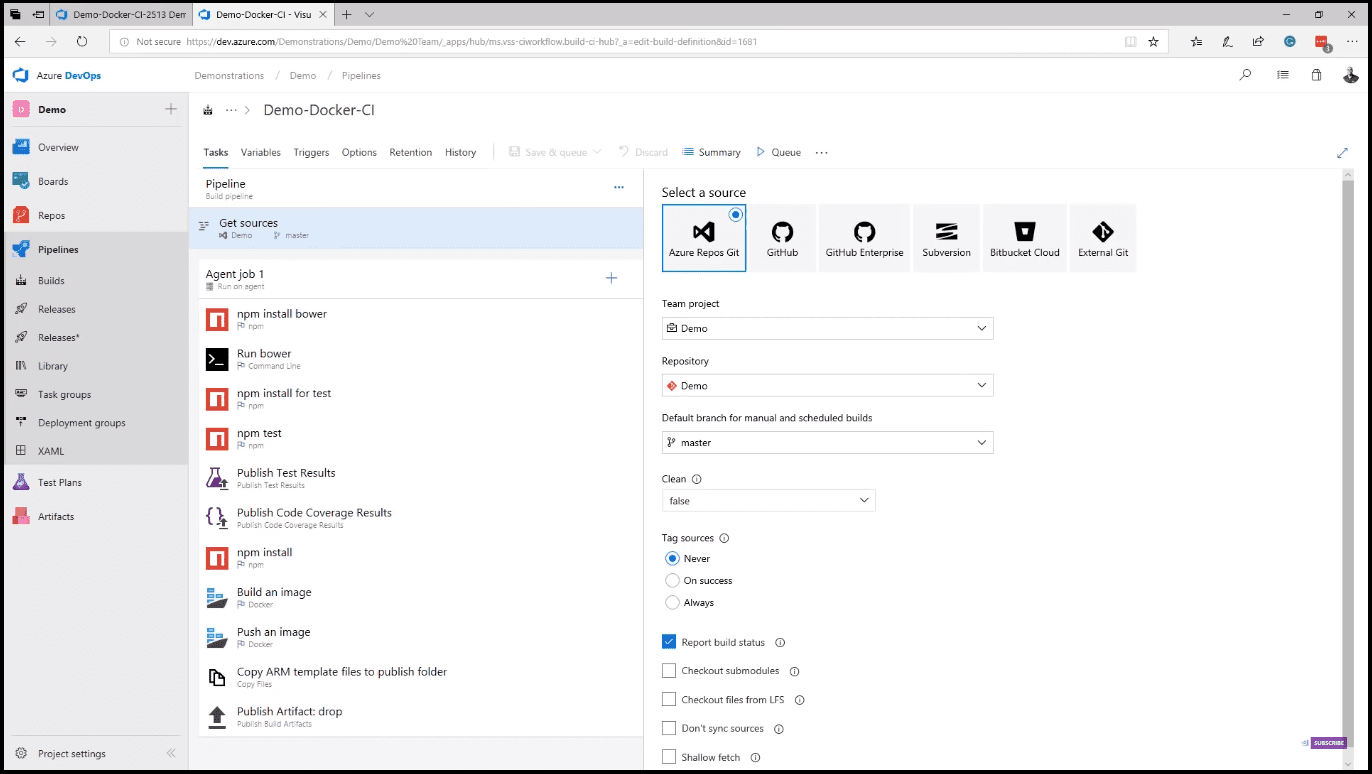
On the summary of a build, you can review the commit test results and much more. The deployment section allows you to see where in the release this build is currently. Editing a build definition is where you start seeing the real power. Azure Pipelines can pull your code from the most popular source control systems (image 8).
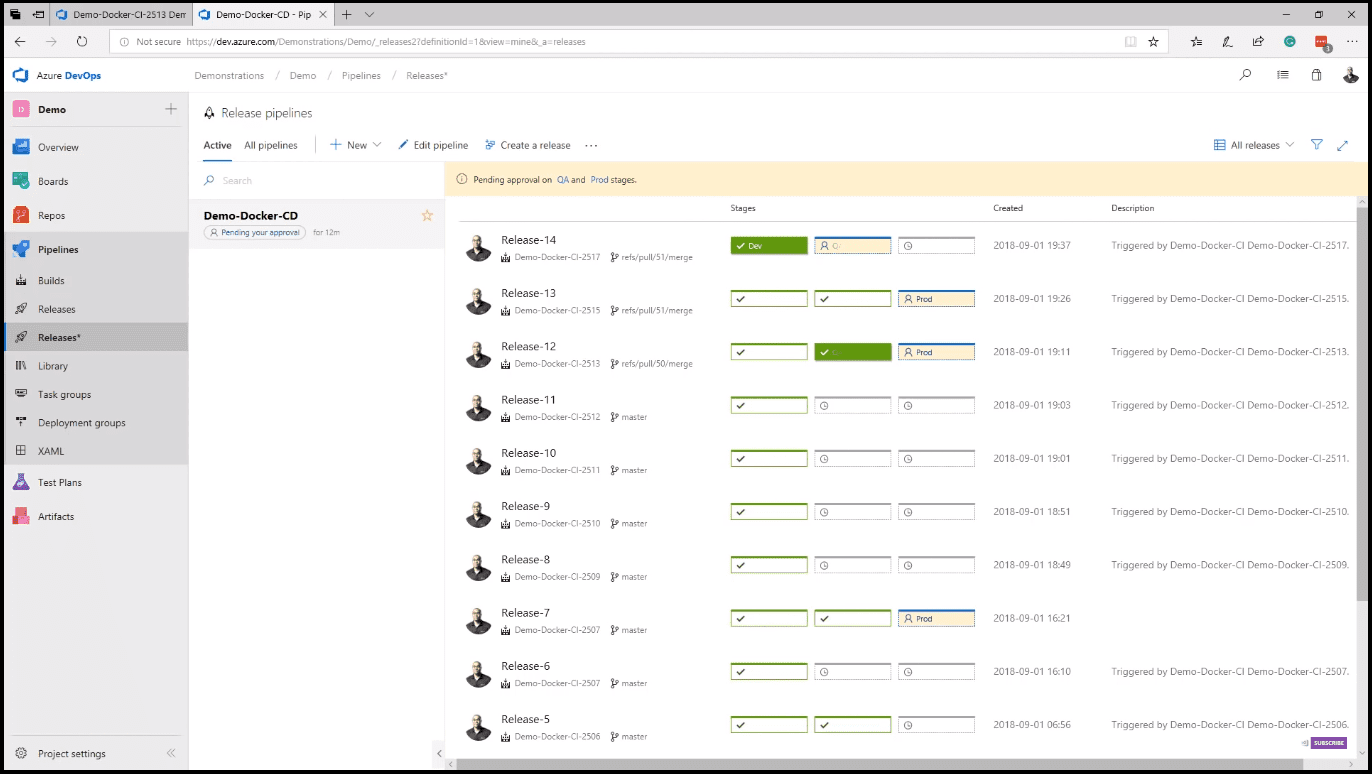
Azure Pipelines also offers hosted Mac OS, Linux, and Windows build agents. Adding tasks to your build is as easy as dragging and dropping from the collection of hundreds of open-source tasks. In case you do not see the task that you need, simply search the marketplace or write your own. Once the build is complete, Azure Pipelines can deploy to any platform with releases. Releases, like builds, provide hosted agents on Mac OS, Linux, and Windows, and with integration with App Center, can deploy to mobile as well (image 9).
You can also edit a release by clicking on the Edit pipeline button. You can pull the artifact to be deployed from almost everywhere, including other CI systems like Jenkins. Releases let you define environments and even assign approvers between them. From releases, you have access to the same rich library of tasks and agents.
Azure Test Plans and Artifacts
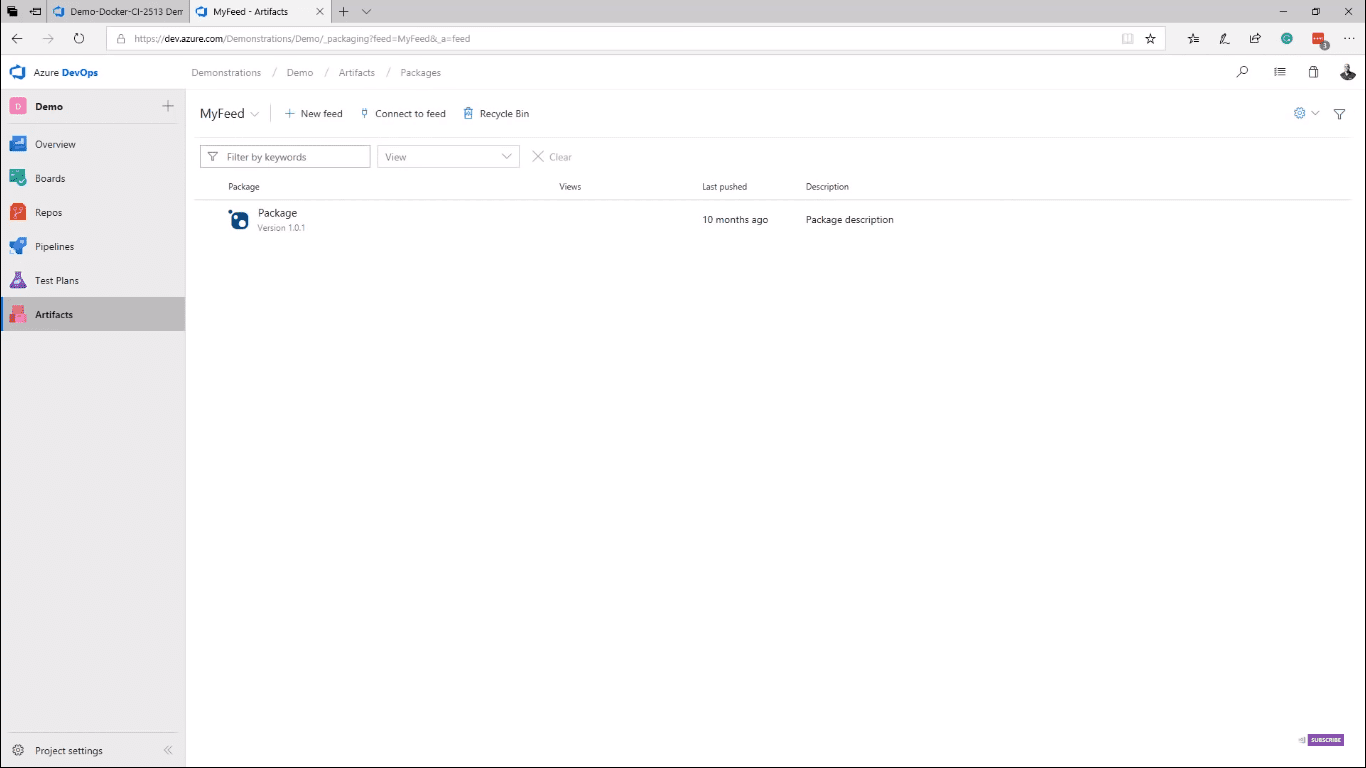
Azure Test Plans allow you to manage your entire testing effort across all your platforms and configurations. Here you can put all your planned and exploratory testing solutions. Azure Artifacts allow you to apply the same DevOps best practices to the packages that you develop and maintain (image 10).
Conclusion
This was just a quick glimpse of what is available from Azure DevOps for any language, targeting any platform. Each Azure DevOps service is open and extensible. They work great for any type of application regardless of the framework, platform, or cloud. You can use them together for a full DevOps solution or with other services. Get started today and see how Azure DevOps can accelerate your DevOps transformation.