Introduction
For those of you that are new to the service, Cosmos DB is a globally distributed multi-model database service that allows you to read and write data from any Azure region with single-digit millisecond latency for both reads and writes.
Developer Update Highlights
.NET SDK Version 3.0 (Preview)
.NET SDK Version 3.0 targets have a new intuitive object model designed to be easier to use, support for streams, performance improvements, and it is open source on GitHub.
Database-Level Throughput - 25x Lower Entry Point
This will enable you to create a new database, put as many containers as you want inside, and have them all share the same throughput of the database.
Azure Pipelines Cosmos DB Emulator Build Tasks
Azure Pipelines Cosmos DB build task allows you to run tests against Cosmos DB emulator in your CI/CD pipelines.
If you would like to know more about Azure deployments, have a look at the post How to Deploy to Azure Using Team Services Release Management. The post describes how Azure deployments are made easy by using Visual Studio Team Services (VSTS) Release Management. You will see a step-by-step tutorial on how to configure and deploy to Azure in Release Management, and moreover, how to configure an end-to-end pipeline for deploying applications on Azure.
A Real Example
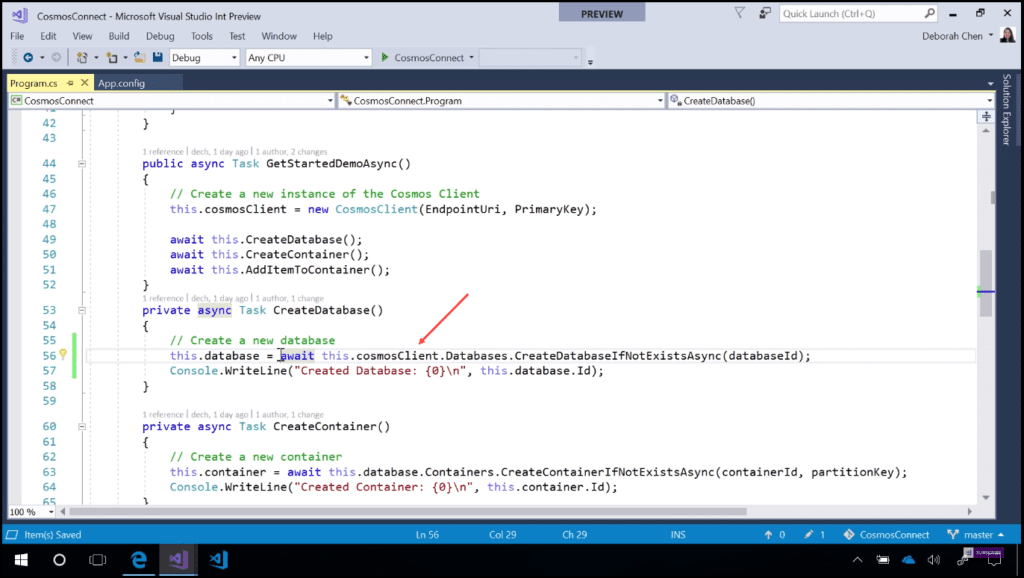
Let’s see an example. Now I am going to create a new database with Cosmos DB in just one line (Image 1). I will start with this.database equal to this.cosmosClient, which is the entry point to interact with a Cosmos DB service. Off this cosmos client, we see that there is a new databases property off which we can access every method relevant to databases. In this case, I’ll use the CreateDatabaseIfNotExistsAsync method, giving the databaseId. I’ll put await in front of it, and now I’ve created a new database in just one line with Cosmos DB.
Image 1 - Create a new database in just one line with Cosmos DB
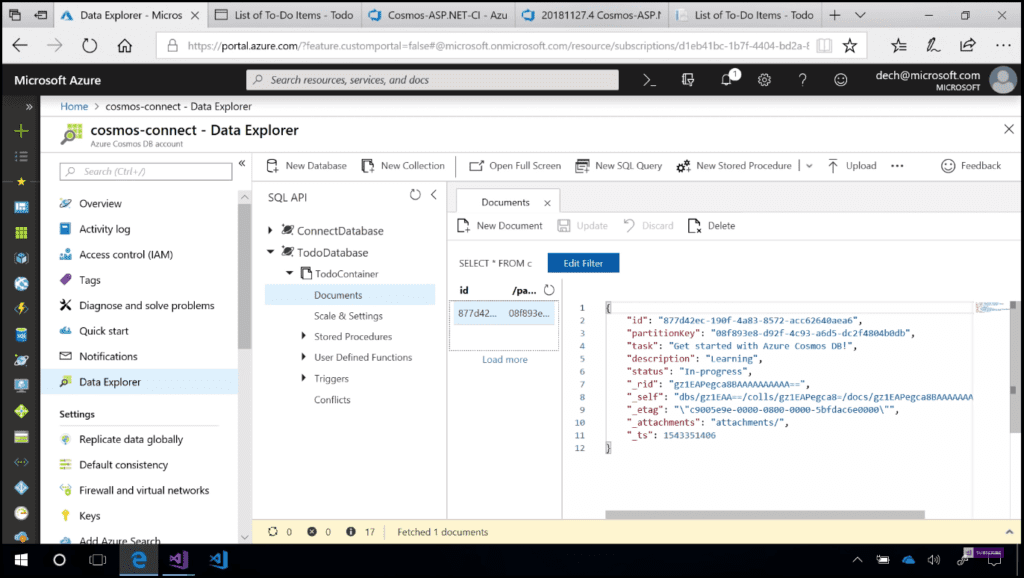
With the new SDK, the object model is updated and the API surface is updated to be more modular. Now as a result, we have a database object, a containers object, and items, each with their own relevant methods. After we run the code, the resources in Cosmos DB (database, container, and item) will be actually created. If we check in the portal, navigate to Data Explorer, which is the one-stop shop for viewing all the data and the Cosmos DB containers. After refreshing, we can see that our “to do” database and “to do” container have both been created. If we open the “Documents” we can see that it is the same item which we created via console app (Image 2).
You can see this video If you would like to find more information about a walkthrough introducing the Release Management and Build Automation using TFS 2017/2015. Step by step about all processes, starting from creating the project, checking in the code into the source control, creating a build definition and triggering the build, and also creating a release pipeline.
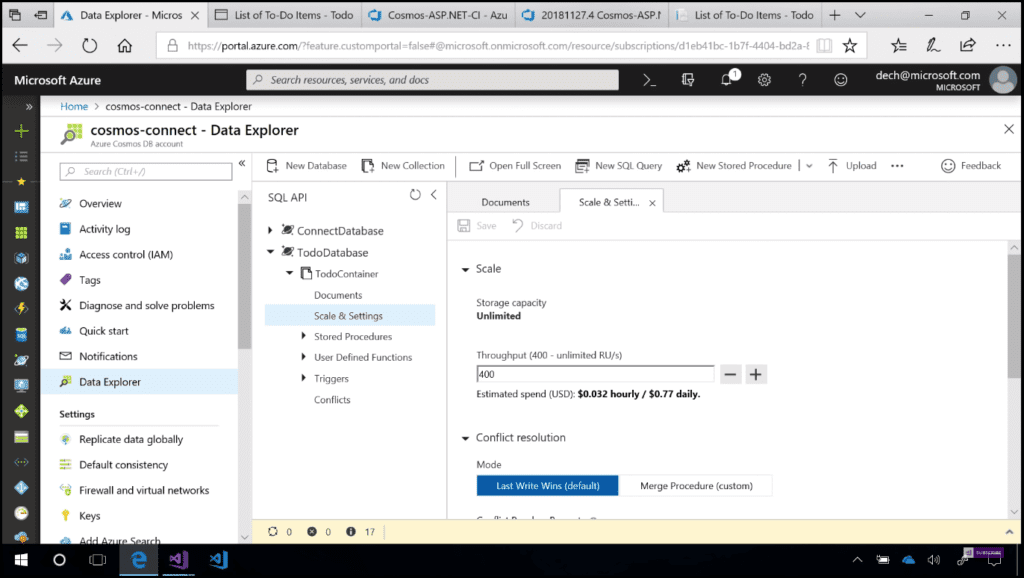
Learn how to configure the build steps properly, including Copy Files and Publish Build Artifacts. See how to create a new release definition, add environments, and link to the build definition. Afterwards, see how to add tasks to the release definition, like Windows Machine File Copy, and configure them properly. If we take a closer look at our “to do” container, if we go to “Scale & Settings”, we can see more information about Scale and Conflict resolution (Image 3).
Next, we will see a dev-test experience with an ASP.NET web application running against Cosmos DB. Actually, it is running against our local emulator. The emulator runs on Windows machines and allows you to emulate the Cosmos DB service locally. So you can do operations like creating databases and containers, running unit tests, etc., without incurring any cost on the Cosmos DB service. Now I will run my already created unit tests, which will create a new container, create a new database, add some items to it, and test a query, running against a local version of the emulator.
CI/CD Pipeline
Now also you can do the same thing in a CI/CD pipeline. I already have a pipeline setup, which builds my web app, runs some tests, and deploys it to Azure App Service. I just need to add my Cosmos DB emulator build task (Image 4), which I can get free from the Azure DevOps marketplace. There I should just specify that I want to use the endpoint emitted by the emulator container earlier in this pipeline.
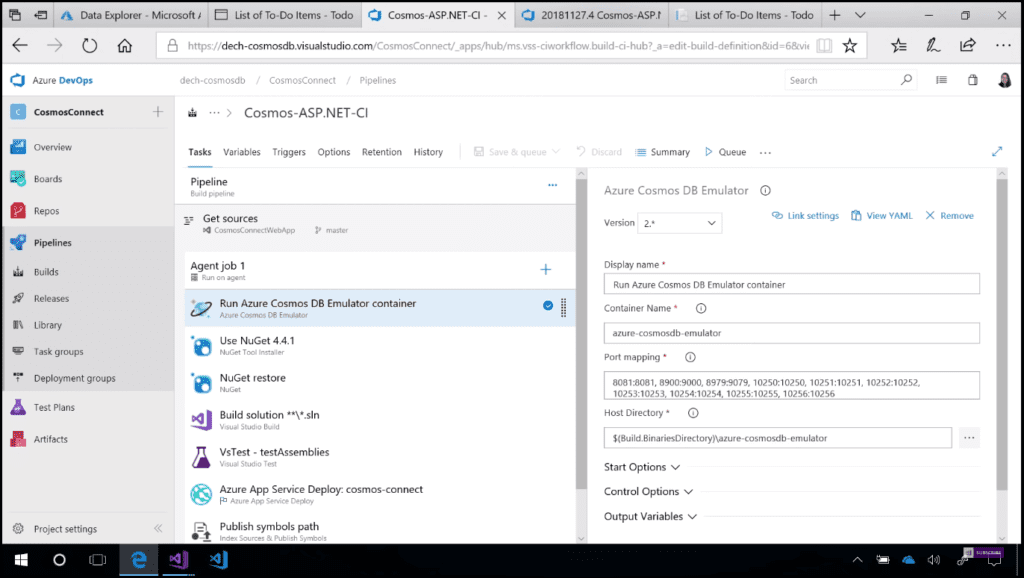 Image 4 - Run Azure Cosmos DB Emulator container
Image 4 - Run Azure Cosmos DB Emulator container
After that, I can queue my build. In Image 5, you can see the log details.
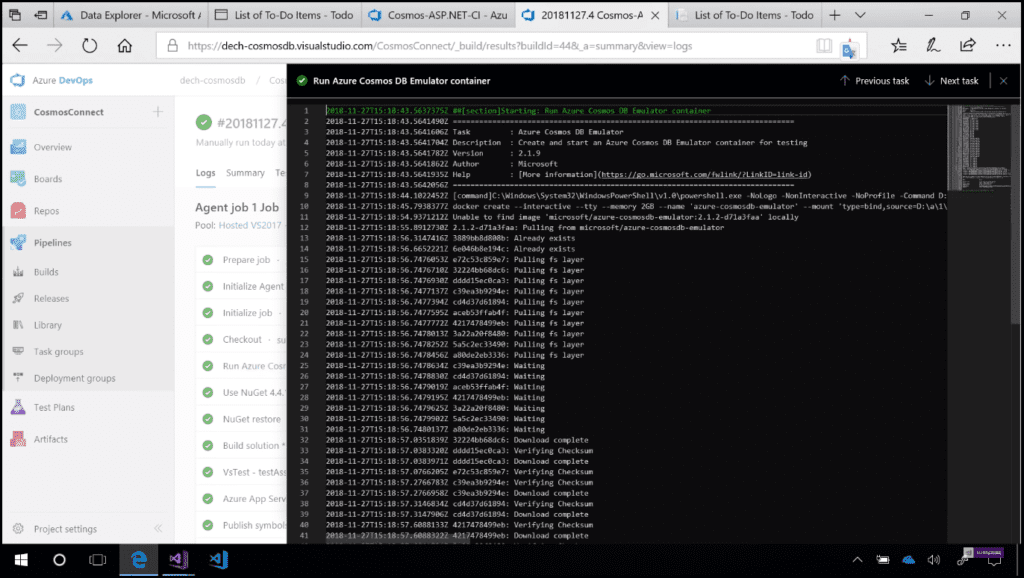 Image 5 - Detailed logs of the Azure Cosmos Emulator DB container
Image 5 - Detailed logs of the Azure Cosmos Emulator DB container
This build task makes it a lot easier to use Cosmos DB in CI/CD, meaning you no longer need to deal with manually setting up a container and manually setting the emulator and getting it to run.
Conclusion
Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft’s globally distributed multi-model database service. With the click of a button, Azure Cosmos DB enables you to elastically and independently scale throughput and storage across any number of Azure’s geographic regions. You can elastically scale throughput and storage. And take advantage of fast, single-digit-millisecond data access using your favorite API among SQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Tables, or Gremlin. You can try Azure Cosmos DB for free without an Azure subscription, free of charge and commitments. Try all the above-mentioned features and stay up-to-date on the latest Azure Cosmos DB news and features.